Basic Premise
For my senior thesis at Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology, I am attempting to combine the fields of Computational Linguistics and Artificial Intelligence in a new and useful manner. Specifically, I am planning on making use of Artificial Neural Networks to enhance the performance of n-gram based document classification. Over the next few months, I will be updating this category with background and information and further progress.
First, I’ll start with some basic background information.
Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
From Wikipedia:
An artificial neural network (ANN), usually called “neural network” (NN), is a mathematical model or computational model that tries to simulate the structure and/or functional aspects of biological neural networks. It consists of an interconnected group of artificial neurons and processes information using a connectionist approach to computation. In most cases an ANN is an adaptive system that changes its structure based on external or internal information that flows through the network during the learning phase. Neural networks are non-linear statistical data modeling tools. They can be used to model complex relationships between inputs and outputs or to find patterns in data.
Example ANN* *
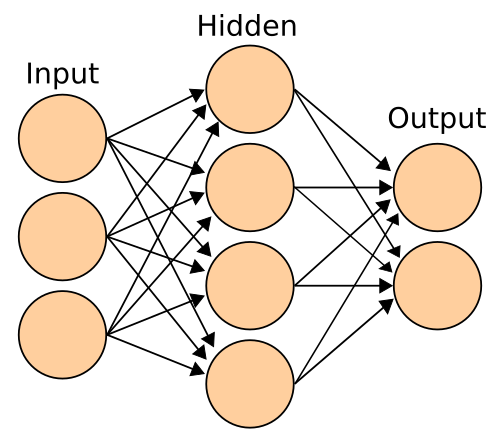
In the above image, the colored circles are individual neurons. The above arrangement is a traditional one, with three layers: input, hidden, and output. The input layer takes input from outside of the system and certain nodes fire based on said input. These nodes then pass their values along to the hidden layer (neither input nor output). The hidden nodes are what allow a neural network to adopt to non-linear problems. These then pass their values along to the output which are sent out from the system.
n-gram
From Wikipedia:
*An n-gram is a subsequence of n items from a given sequence. The items in question can be phonemes, syllables, letters, words or base pairs according to the application.
An n-gram of size 1 is referred to as a “unigram”; size 2 is a “bigram” (or, less commonly, a “digram”); size 3 is a “trigram”; and size 4 or more is simply called an “n-gram”. Some language models built from n-grams are “(n - 1)-order Markov models”.
An n-gram model is a type of probabilistic model for predicting the next item in such a sequence. n-grams are used in various areas of statistical natural language processing and genetic sequence analysis.*
**Example ****n-gram **
As an example, consider “ROSE-HULMAN” with the following 4-grams:
- ROSE
- OSE-
- SE-H
- E-HU
- -HUL
- HULM
- ULMA
- LMAN
One of the most interesting features of n-grams is that they encode not only the letters and words used by the author, but also the relationships between them. As such, n-grams can be used to paint a more complete picture of an author.
Future Plans
- Describe prior algorithms
- Implement prior algorithms as benchmarks
- Add neural networks
- Tune efficiency